Our new QoS sensor measures the following network connectivity parameters:
- Jitter in ms according to RFC 3550
- Packet delay variation (PDV) in ms according to RFC 3393
- Lost packets in %
- Reordered packets in %
- Duplicated packets in %
Sample Charts
Look at the following three charts which compare three network connections: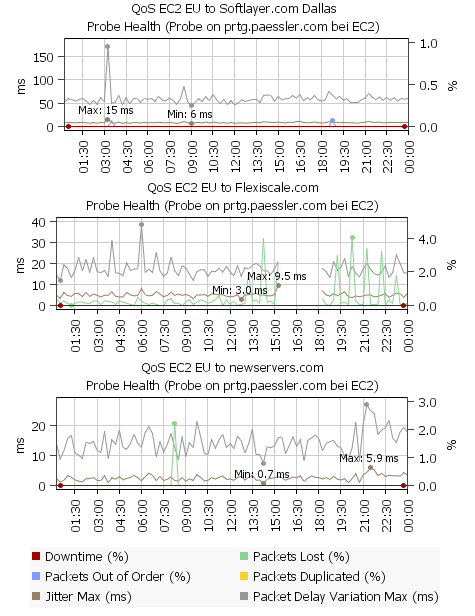
- Chart 1 - EC2 EU to Softlayer: Jitter is very good (around 10 ms), packet delay variation a little high with 50ms. And there were two short moments where reordered packets occured (at 3:30 and 18:45).
- Chart 2 - EC2 EU to Flexiscale: Jitter is ok, PDV shows some variation during the day. But there is a notable and steady packet loss (up to 4%) which tells us that the quality of this connection is not very good.
- Chart 3 - EC2 EU to newservers.com: Jitter (~2 ms) and PDV (~10ms) are very low and there is only one short period of packets loss at 8:45.
How To Set Up Qos Sensors
Measurement takes place between two probes. So the first step is to place two PCs running a remote probe on (or near) both ends of the connection that you want to monitor (the local probe on the PC running the PRTG Core can also be used). If any firewalls, packet filters or NAT systems are en-route you must configure them as necessary so that the UDP packets can reach the target probe. In PRTG new QoS sensors must be created with a "probe device" as the parent device. The UDP packets will be sent from this probe to the target probe. During the creation of the sensor you are going to choose the target probe that the UDP packets shall be sent to for measurement. To get started right click a probe device, choose "Add Sensor" and then choose "QoS sensor" from the "Infrastructure" group. On the next web page you can configure the sensor: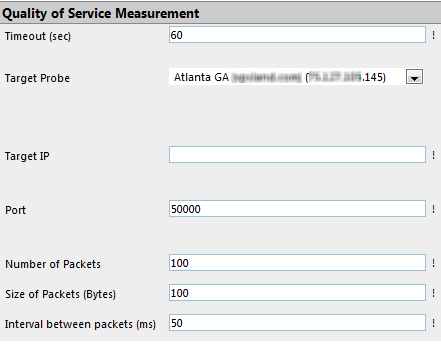
 Published by
Published by