Ping is a basic network troubleshooting utility. Ping sends an ICMP echo request and waits for an ICMP echo reply. It's really that simple. But in that simplicity lies great power. Ping tests the network path between two devices, allowing users to test and diagnose connectivity issues.
i Ping is available as a command line tool on just about any network-enabled operating system, including Linux, macOS, and Microsoft Windows. Ping essentially tests if other network devices are reachable. Ping uses Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) echo request data packets to send information over the network to a device. If the destination device responds, the ping test is successful and returns ICMP echo replies. Read more ...
Ping The Host
The first step in troubleshooting connectivity with ping is to test reachability to the remote host by simply pinging the hostname (IP address). Important: Some devices will not respond to ping requests. Confirm your target device will respond to ICMP echo request messages. If the ping command is successful and returns ping replies, then network connectivity is working correctly, and any issues lie elsewhere in the network stack.
Syntax: Type ping in the command prompt followed by the hostname or IP address you want to reach.
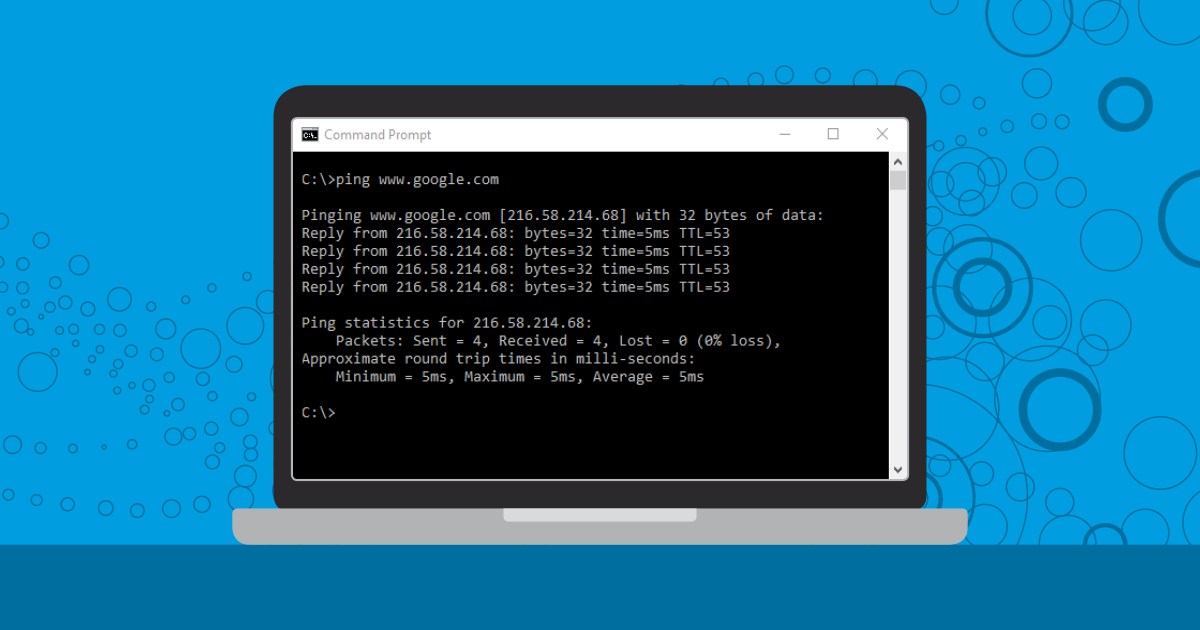
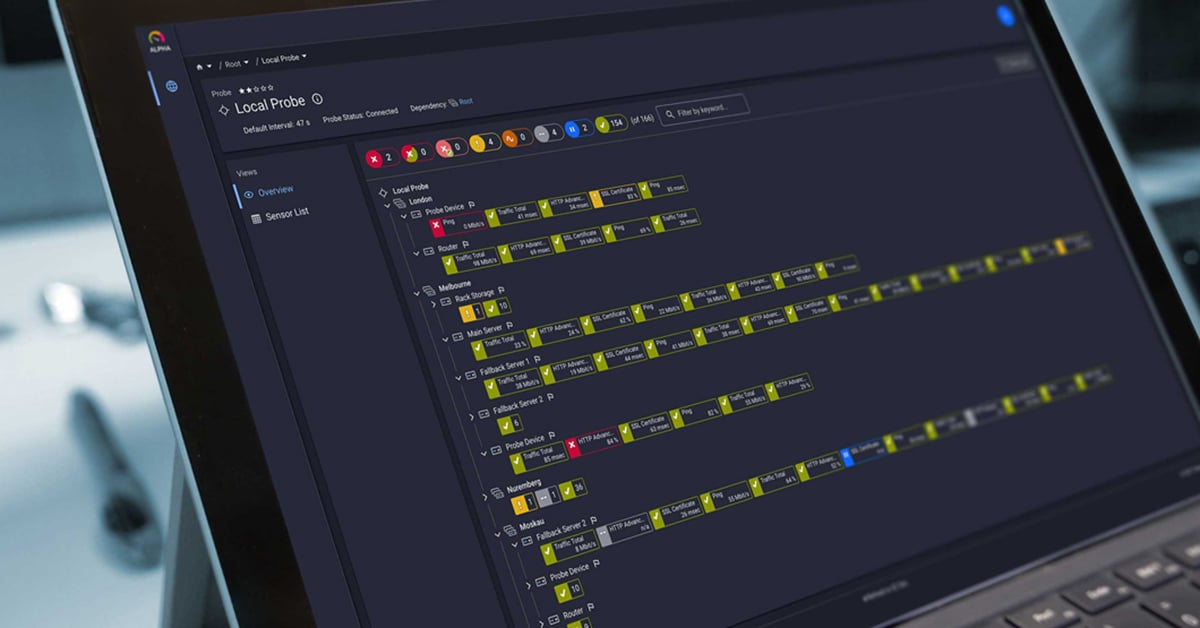
Ping uses a destination host name or IP address, so if you're having trouble connecting to a particular website, you can ping the domain name to see if it is up and running (example shown below).
The 4 replies in this test show the server is reachable, network connectivity and internet connection are working. The response time tells us network connectivity to the server is good, and round-trip latency is reasonable. If webpages are not loading, then the problem is likely server configuration instead of a network problem.
Ping By IP Address
Ping commands send requests directed specifically toward the designated IP address. This is the next troubleshooting step. If you can ping a host by its IP address but not the hostname, the problem is with DNS name resolution. In the example above, if I can ping the IP address but not the domain name, my problem is with name resolution, and perhaps I have a misconfigured DNS server.
What Else Ping Tells Us
In the example above, 4 ping requests were sent and 4 replies were received. The output also lists round-trip time for the ping requests, showing low latency in the 13-23 ms range. Large spikes in response time indicate possible network congestion or other connectivity issues. Ping response time can vary greatly depending on the environment but a large jump over typical latency would indicate a problem.
Packet loss is not ideal but when only a few ping requests out of many return success, that indicates local network or internet connection problems. But if a ping command returns some successful replies, at least the network is partly configured correctly.
Common ping error messages and their meanings:
- "Request timed out" - The target device didn't respond within the timeout period. This could indicate network congestion, firewall blocking ICMP traffic, or the target device being offline.
- "Destination host unreachable" - Your computer cannot find a route to the target. Check your network configuration and routing tables.
- "General failure" - Usually indicates a problem with your local network adapter or network configuration.
- "Ping request could not find host" - DNS resolution failure. The hostname cannot be resolved to an IP address.
Understanding ping failure messages helps with quick diagnostics of if the problem is local to the source computer, network related, or the target system.
Note: In most corporate firewalls, ICMP traffic is blocked by default. This can result in failed ping tests even if network connectivity is present.
Troubleshoot Network Connectivity Issues with Ping
Ping network troubleshooting is valuable but knowing where in the network connectivity breaks down is even better. Network administrators can get a better idea about where network issues are occurring by pinging key parts of the network infrastructure.
Use this methodology for step by step ping troubleshooting of networks. Ping each key element of the network starting with the source device itself, then the network, and then remote sites.
| Step | Target | Command example | What it tests |
| 1 | Loopback | ping 127.0.0.1 | Local network stack |
| 2 | Local IP | ping [your IP] | Network Interface* |
| 3 | Gateway | ping [gateway IP] | Local network connectivity |
| 4 | External DNS | ping 8.8.8.8 | Internet connectivity |
| 5 | Domain name | ping google.com | DNS resolution |
* Note: Step 2 may not work identically across all network configurations, particularly with certain network adapters or virtualized environments.
IPv6 Networks: For IPv6 environments, use ping6 command on Linux/Unix or ping -6 on Windows, and test IPv6 addresses like 2001:4860:4860::8888 (Google's IPv6 DNS).
If Step 1 fails, you have a local system problem. If step 3 fails and 1-2 succeed, local network connectivity is bad or ICMP is being blocked. This ping testing methodology quickly isolates where connectivity problems are in a network.
Important: This assumes IPv4 only networks. In more locked-down networks, ICMP traffic may be blocked by firewalls, which can cause ping to fail even when other network connectivity is functioning. When ICMP is blocked or not present, it is helpful to use other network connectivity tests like telnet [host] [port] to test specific services instead of ICMP.
Keeping Pinging!
An important technique when using ping for network troubleshooting is setting a continuous ping. This is useful in many situations, for example if you want to make sure a remote host stays reachable or to monitor when it becomes unreachable.
Administrators can set a computer to continuously ping a remote host while they make changes to wiring or test network devices. If ping requests stop returning, then the change has broken the previously working network.
To continuously ping with Windows, use the -t switch.
ping -t URL.
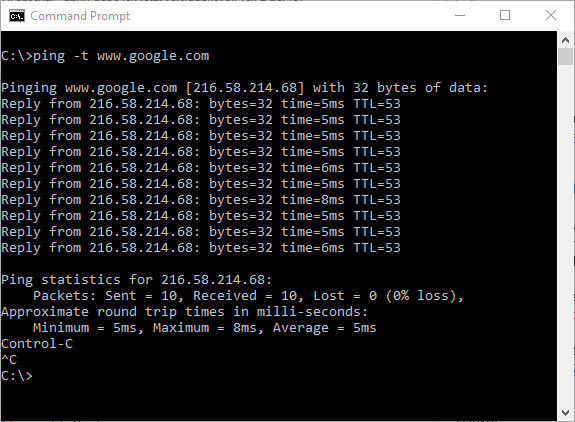
Press Ctrl-C to stop the ping or close the command window.
Additional continuous ping options:
Windows advanced parameters:
- ping -t -l 512 hostname - Continuous ping with larger packet size (512 bytes avoids most MTU issues)
- ping -n 100 hostname - Send exactly 100 pings then stop
Linux/Unix equivalent:
- ping hostname - Runs continuously by default on most distributions
- ping -c 100 hostname - Send exactly 100 pings
- ping -i 0.5 hostname - Ping every 0.5 seconds (may require root privileges on some systems)
Technical Note: Some of the advanced ping parameters may require administrative/root privileges. Basic connectivity testing is available with normal user privileges.
To stop a continuous ping test, press Ctrl-C on any system. Continuous ping is especially helpful when testing network changes, as you can see when the network connection goes down or comes back up in real-time.
Advanced Network Ping Testing
Here are some additional tools for administrators who want to go further with network ping testing:
- Traceroute/tracert: Shows the network path packets take to the remote host
- TTL analysis : Time-to-Live can identify routing issues
- Ping statistics : Packet loss patterns and latency
Ping From Multiple Global Locations
Ping is a great tool for network troubleshooting, but for it to be the most reliable, it's necessary to ping from multiple global locations. Let's say your server is in Germany. A ping response time result from a site in Germany is going to be lower in milliseconds (fast) when compared to a response time you get if you ping from China.
Ping Speed Test from all over the world - An easy way to test response time from different locations globally is our new Ping Speed Test . We use ping to send data packets from every continent. The result? Insight into response time minimum, maximum, and average plus an explanation of what is a good ping speed.
And now it's getting exciting. Want to know what the current ping times are for your (or any) website? Then take a look at our brand new ping test tool and see how ping times can be improved in your individual case.
 Published by
Published by