If you're running Veeam Backup & Replication on a Windows Server backup repository, you're probably watching storage costs climb every quarter. Synthetic full backups eat disk space. Backup chains grow. And eventually, you're either buying more storage or deleting older restore points sooner than you'd like.
We hit that wall last year—hard. Our Veeam backup server was choking on 20TB of backup data, and our CFO was asking why we needed another SAN expansion. The answer? We didn't. We needed a smarter file system.
This article walks through both sides of the equation: how ReFS transforms Veeam backup storage through fast clone technology, and how PRTG gives you complete visibility into your Veeam ReFS environment—so you catch backup failures before disaster strikes, not after. (New to backup monitoring? Check out our guide on several options to monitor your backup with PRTG.)
Why Veeam ReFS Integration Matters for Backup Repositories
When Microsoft introduced ReFS (Resilient File System) in Windows Server 2016, it wasn't just another file system. It was built specifically for modern workloads like virtualization, backup storage, and large-scale data services—things NTFS was never designed to handle efficiently.
Here's what makes ReFS different for Veeam backup repositories (you can dive deeper into the technical details in Microsoft's ReFS documentation):
Block-level integrity. ReFS uses metadata checksums and copy-on-write architecture. Your backup files get continuous integrity verification without manual scrubbing.
Block cloning API. This is the killer feature. When Veeam creates a synthetic full backup or runs incremental backups, ReFS doesn't copy entire data blocks—it clones pointers to existing blocks. A 2TB synthetic full backup that would normally write 2TB to disk? With ReFS block cloning, it writes only the changed blocks and creates metadata pointers for everything else.
Space savings at the file system level. Unlike deduplication (which requires additional processing and memory overhead), ReFS block cloning happens natively. No extra CPU cycles. No RAM tax. Just instant space savings when Veeam triggers synthetic operations.
Scalability. ReFS supports massive volumes—up to 4.7 zettabytes with Windows Server 2019. Your backup storage can grow without hitting NTFS limitations.
Here's the reality check: NTFS still works fine for many Veeam deployments, especially smaller environments with limited backup retention. But if you're running:
- VMware or Hyper-V workloads with dozens of VMs
- GFS (Grandfather-Father-Son) retention schemes that pile up synthetic fulls
- Per-VM backup chains that replicate to secondary repos
- Multi-site Veeam environments where storage efficiency directly impacts your budget
...then Veeam ReFS integration isn't optional. It's your best defense against spiraling storage costs.
How ReFS Block Cloning Transforms Veeam Backup Storage
Let's get technical for a minute. You need to understand how synthetic full backups work to appreciate what ReFS block cloning actually does.
Traditional Synthetic Full Backups (NTFS or Other File Systems)
You've configured your Veeam backup jobs like most people do:
- Daily incremental backups Monday through Saturday
- Weekly synthetic full backup every Sunday
On Sunday, Veeam reads every block from the previous full backup, adds all the blocks from the week's incremental backups, and writes a brand-new full backup file to disk. It's called "synthetic" because you're not hitting production systems again—you're creating the full backup from existing backup data.
Sounds efficient, right?
It is. Compared to running an active full backup against live servers every week, synthetic operations save massive amounts of network traffic and production system load.
But here's the problem: every block still gets written to disk. If your full backup is 2TB, Veeam writes 2TB of data even if 80% of those blocks already exist in last week's full backup. You're duplicating data at the file system level.
Veeam ReFS Fast Clone (Block Cloning in Action)
Now let's see what happens when you point Veeam at a ReFS volume.
When Veeam triggers a synthetic full backup on a ReFS repository, it uses Microsoft's block cloning API. Instead of writing duplicate data blocks to disk, ReFS creates metadata pointers that reference the existing blocks.
Here's the breakdown:
- Unchanged blocks: ReFS creates a pointer. Storage consumed = metadata only (a few KB).
- Changed blocks: ReFS writes the new data and creates a pointer to it.
- Result: Your 2TB synthetic full backup might consume only 200GB of new storage, depending on your change rate.
The backup file still appears to be 2TB from Veeam's perspective. You can restore from it just like any other full backup. But at the file system level, you're only storing unique data blocks once.
This is completely transparent to Veeam Backup & Replication. The Veeam software doesn't need special configuration. It just calls the Windows API, and ReFS handles the magic behind the scenes.
Real Results: 50% Space Savings with Our Veeam ReFS Repository
Before switching to ReFS: 19.2TB of backup data consuming 19.2TB of physical storage.
After switching to ReFS: 19.2TB of backup data consuming 9.2TB of physical storage.
That's a 52% reduction in actual disk usage. Your mileage will vary based on your backup retention policies, VM change rates, and whether you're running backup copy jobs or replication tasks, but most Veeam users see 40-60% savings when moving from NTFS to a ReFS repository.
One more thing: this isn't deduplication. ReFS block cloning doesn't require post-processing, rehashing, or memory-intensive lookups. It happens in real time as Veeam writes backup files. Zero performance penalty.
Monitor Your Veeam ReFS Environment with PRTG (Because Backups Are Only Good If They Actually Work)
You know this pain: you discover a failed backup job three days too late, right when someone needs to restore a critical VM.
Or worse—your Veeam backup server is low on disk space, backup jobs start failing, and nobody notices until alerts start firing from production systems that can't reach their backup window.
Look, storage savings don't matter if your backup infrastructure isn't reliable. And reliability requires monitoring. Not "check it when you remember" monitoring. Real-time, 24/7, proactive monitoring that catches issues before they become outages.
PRTG Network Monitor gives you three layers of visibility into your Veeam ReFS environment:
- Hardware health (your physical backup server and storage)
- Veeam application monitoring (backup jobs, repositories, and replication tasks)
- ReFS savings tracking (so you know exactly how much space block cloning is saving you)
Here's how to set it all up.
Layer 1: Hardware Monitoring for Your Veeam Backup Server
Your Veeam software runs on something—usually a Windows Server physical box or a VM with direct-attached storage. That infrastructure needs to stay healthy, or your backups stop.
PRTG's built-in sensors handle this automatically:
- Ping Sensor: Verifies network connectivity to your backup server
- Windows CPU Load Sensor: Tracks processor usage during backup windows
- Windows Memory Sensor: Monitors RAM utilization (synthetic operations can be memory-intensive)
- Windows Physical Disk I/O Sensor: Tracks disk read/write operations on your ReFS volume
- Windows Pagefile Sensor: Catches memory pressure issues before they slow down backups
- Windows Uptime Sensor: Alerts if your backup server reboots unexpectedly
With the Windows Physical Disk I/O Sensor, you can track read/write operations and spot performance bottlenecks before they impact backup windows. And if you need comprehensive disk space monitoring across your infrastructure, PRTG covers everything from local drives to SAN arrays.
If you're using Storage Spaces, a RAID controller, or iSCSI for your Veeam backup repository, add those to PRTG too. You want full visibility into the storage stack.
Layer 2: Veeam Application Monitoring (The Part That Actually Matters)
Hardware health is table stakes. What you really need to know is: Did my backup jobs run successfully? Are my restore points valid? Is my Veeam backup repository running out of space?
PRTG's Veeam Backup Sensor answers all of that. It's an EXE/Script sensor powered by a PowerShell script that pulls data directly from the Veeam Backup & Replication API.
The sensor monitors:
- Backup job status: Success, warning, or failure for each configured job
- Backup copy jobs: Whether secondary copies completed successfully
- Replication tasks: VM replication health for disaster recovery scenarios
- Repository status: Free space on your ReFS repository, capacity trends, and alerts before you hit thresholds
- Backup file size: Track growth over time to predict storage needs
You can grab the PowerShell script from the PRTG Sensor Hub—it's open source, and it works with Veeam Backup & Replication v9.5 and later (including current versions supporting Windows Server 2019 and Hyper-V / VMware / ESXi environments).
Set the sensor to run every 30 minutes. If a backup job fails, you get an alert immediately. Not three days later when someone tries to restore a file.
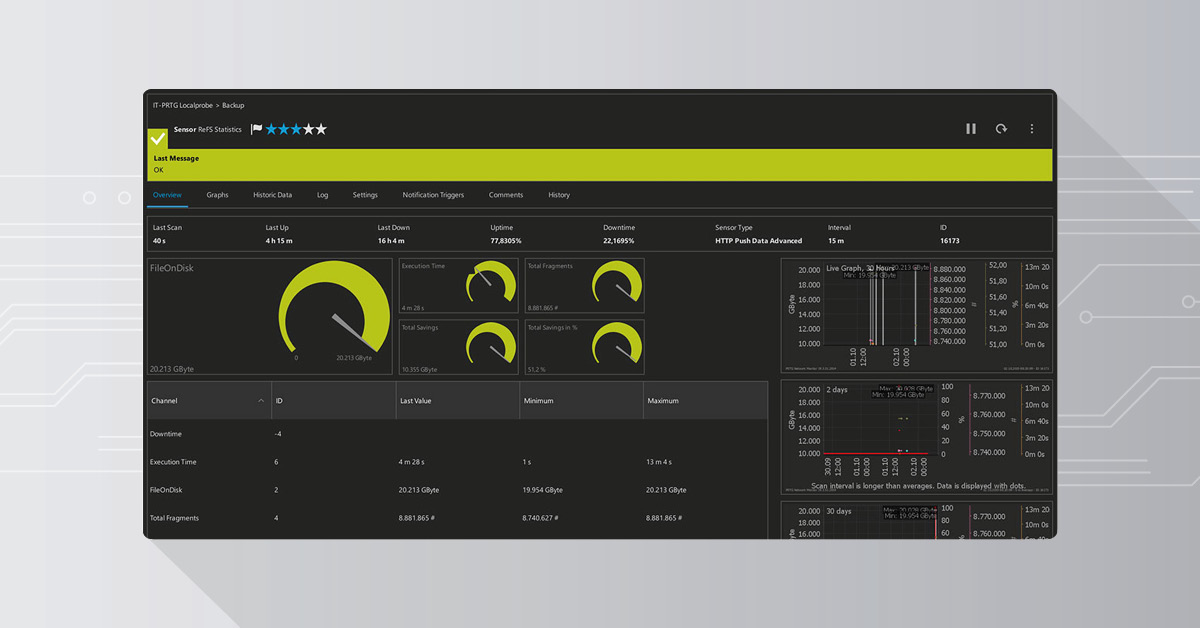
Layer 3: Track ReFS Space Savings in Real Time
This is the part most people skip, but it's incredibly useful: monitoring exactly how much storage your ReFS block cloning is saving.
PRTG doesn't have a built-in "ReFS savings" sensor, but you can build one in about 10 minutes using an HTTP Push Data Sensor and a scheduled PowerShell script.
Here's how it works:
- Create an HTTP Push Data Sensor in PRTG. This sensor waits for data to be pushed to it via HTTP POST.
- Run a PowerShell script on your backup server (daily via scheduled task) that calculates ReFS space savings using Microsoft's
blockstat.exeutility. - The script pushes the results to PRTG, and you get a real-time graph of total savings and fragmentation over time.
We've packaged everything you need into a single download: the PowerShell script, the blockstat.exe tool, and a helper script to create the scheduled task automatically.
5 Steps to Deploy ReFS Savings Monitoring
- Download the ReFS monitoring script package (link in resources below)
- Create an HTTP Push Data Sensor in PRTG and configure it to accept POST requests
- Extract the files to your Veeam backup server (we recommend
C:\Scripts\ReFS-Monitoring\) - Run the
Create-ScheduledTask.ps1script and follow the prompts to set up a daily scheduled task - Check PRTG—within 24 hours, you'll see your first data point showing total savings and block fragmentation
The script works with any ReFS volume, not just Veeam repositories. If you're running ReFS for SQL Server databases, Hyper-V storage, or file shares, you can monitor those too.
Veeam ReFS Best Practices (What We Learned the Hard Way)
Switching to ReFS isn't just "reformat and go." Here are a few gotchas we hit:
ReFS volumes aren't bootable. Don't try to install Windows Server on a ReFS partition. Use NTFS for your OS, ReFS for your Veeam backup repository.
ReFS doesn't support compression or encryption at the file system level. If you need encryption, handle it at the Veeam level (Veeam supports backup encryption natively) or use BitLocker on the volume.
Cluster size matters. When formatting your ReFS volume, use a 64KB cluster size. Veeam recommends this for optimal block cloning performance.
Storage Spaces work great with ReFS. If you're building a new Veeam backup server, consider Windows Storage Spaces Direct with ReFS instead of traditional RAID. You get both resiliency and block cloning benefits.
Monitor your backup server's RAM. Synthetic operations can be memory-intensive, especially during active full or synthetic full backups. Make sure your server has enough RAM, and use PRTG to track memory usage trends.
Test your restores. ReFS block cloning doesn't change how Veeam restores work, but you should still verify restore operations regularly. PRTG can't test restores for you—that's still on your checklist.
Why PRTG for Veeam Monitoring? (And Why It Matters for Systems Engineers)
You've got a lot of monitoring options. Veeam ONE. Veeam Backup Enterprise Manager. Even custom PowerShell scripts that email you when something breaks.
So why PRTG?
Because you're not just monitoring Veeam. You're monitoring:
- The network your backup traffic runs on
- The physical server or VM running Veeam Backup & Replication
- The storage array or direct-attached storage hosting your ReFS repository
- Your production VMware ESXi hosts, Hyper-V clusters, or physical servers being backed up
- Your secondary backup repositories (maybe a NAS, maybe AWS, maybe Azure)
- Your WAN links if you're running backup copy jobs to remote sites
PRTG monitors all of it in one dashboard. Not just Veeam. Not just your backup server. Your entire infrastructure.
And here's what matters for systems engineers like you:
Deploy monitoring in minutes. PRTG's auto-discovery finds your devices automatically. Pre-configured sensors for Windows, VMware, Hyper-V, and Veeam mean you're not writing monitoring scripts from scratch.
No coding required (but PowerShell is supported if you want it). The Veeam sensor uses a PowerShell script you can customize. But you don't have to. It works out of the box.
Alerts that actually help. PRTG lets you set intelligent thresholds. Alert me if a backup job fails. Alert me if my ReFS volume drops below 15% free space. Don't alert me for every minor warning.
Works with your existing tools. PRTG integrates with ServiceNow, Slack, PagerDuty, and basically any ITSM platform via API or webhooks. Your backup alerts can flow into your existing incident management workflow.
Supports hybrid and multi-site environments. If you're running Veeam across multiple datacenters, branch offices, or cloud providers, PRTG gives you unified visibility. One console. Not five different monitoring tools.
Start Monitoring Your Veeam ReFS Environment Today
ReFS block cloning is a game-changer for Veeam backup storage. It saved us 10TB of disk space and cut our backup storage costs nearly in half. If you're running Windows Server 2016 or later for your Veeam backup repository, there's no reason not to use it.
But storage savings alone won't keep your backups reliable. You need visibility. You need to know when backup jobs fail, when repositories fill up, and when your backup server hits resource limits.
PRTG gives you that visibility—across your hardware, your Veeam software, and your ReFS savings—in a single, unified monitoring platform.
Ready to see it in action? Download PRTG and start monitoring your Veeam environment in under 10 minutes. No professional services. No complex setup. Just immediate visibility into your backup infrastructure.
Start your free PRTG trial now and see how proactive monitoring protects your backups—before you need them.
 Published by
Published by