Frequent cybercrime news reports, and also surveys, show that the human factor in IT Security Management (ITSM) is often given too little consideration. Often, the weakest link in the chain are the employees of an organization and not the IT infrastructure itself. This fact leads directly to the question of “how a comprehensive IT security culture can be developed and maintained within an organization”. Some key aspects to be considered.
Support of The Top Management
Top management needs to support and facilitate the programs for the IT Security Culture and needs to insist on the compliance of the security guidelines.
Setting up Security Guidelines
The definition of roles and responsibilities of all stakeholders provide the base for a IT security conformity behavior.
IT Security Awareness
The IT security awareness is the essential part of the culture. Only if people are aware of the risks and consequences of interaction with IT systems can the overall IT security risk be reduced. Clearly communicated and updated security guidelines raise the IT security awareness in the organization.
IT Security Training
The most effective tool is IT security training that develops the IT security culture in an organization. For a healthy culture, appropriate training for the individual members of the organization should be held regularly – simply because the framework of IT security continually changes. And as always, wider involvement has the greatest impact.
IT Security Risk Analysis
Analyzing and benchmarking security risk of course helps to estimate potential damage, but also promotes an IT security culture.
As we saw in the considerations above, IT security is a process – it never stops and is in constant change. The PDCA (Plan Do Check Act) method can be used to ensure a constant adaption of the framework for a healthy IT security culture.
Plan
First of all an analysis of the current situation is required. And also, the definition of the target state identified in order to outline measures. It is not enough to just check the security guidelines. One must also conduct interviews, observations, and measurements of the behavior should be included in order to get a real picture of the current IT security culture. Depending on the difference between the current and target state, different measures will need to be applied.
Do
In this phase the defined measurements need to be realized. A clear and proactive communication, and the support of the top management, is very important in this phase.
Check
This is the controlling phase of the implemented measures. It is important to verify if the target state was reached by using the same methods as in the planning phase for identifying the current situation.
Act
In the last phase the successfully made changes should be communicated and the learnings shared. This phase also allows for minor corrections of the implementation.
After this very theoretical listing, here is an example:
Organizations face a typical data protection risk when employees work from their laptops remotely, for instance, onboard an airplane. Neighbors – called visual hackers – can easily obtain information which might be highly confidential. How to meet this risk with the PDCA method? 
In phase one, the Plan phase of the PDCA, this potential risk was discovered during an interview. The target state: No visual hacking. A guideline instructing the employee to not work while onboard an airplane won’t be accepted, as the priority of the employee is to get the job done. Therefore, a more successful measure would be to apply a privacy filter to each laptop.
In the Do phase, the IT department can include the privacy filter in the standard equipment list for new employees.
The Check phase should include verification – whether all existing Laptops were equipped with a privacy filter, and whether the filter was included in the IT equipment check list for new laptops.
Not only is the risk in this way reduced automatically, but is further aided by the clear communication during the Act phase. Additionally, by how the privacy filter makes employees more aware of visual hackers and thus strengthens the IT security culture.
Do you have any examples for cases where you have used the PDCA method? Please share in the comments section!
 Published by
Published by 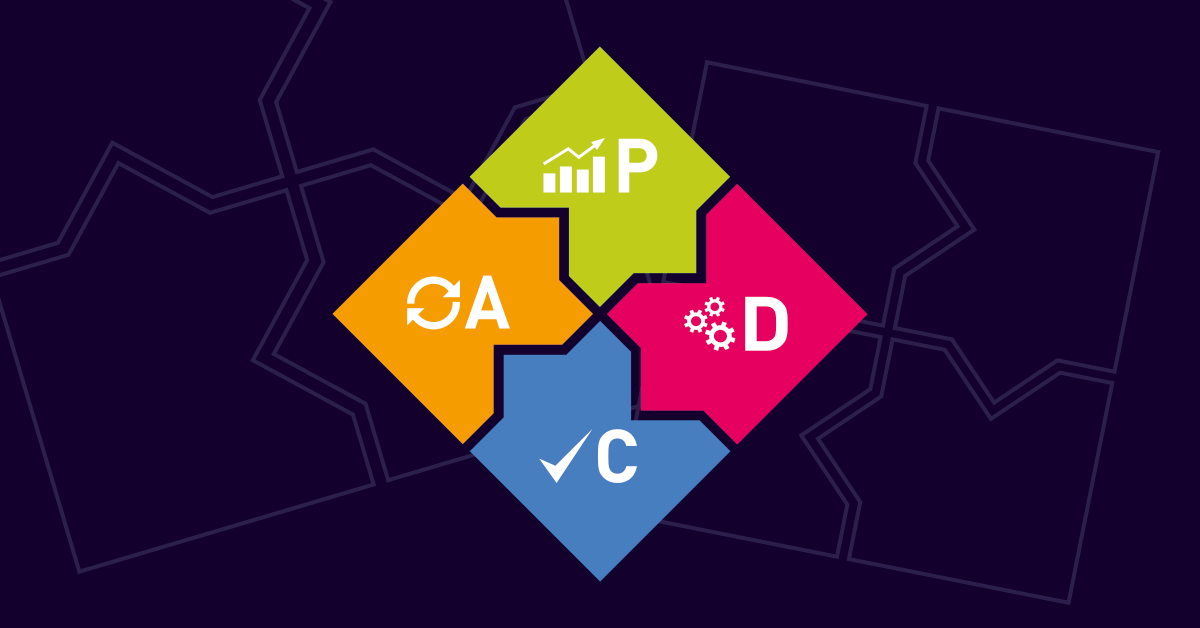



.jpg)